Abstract
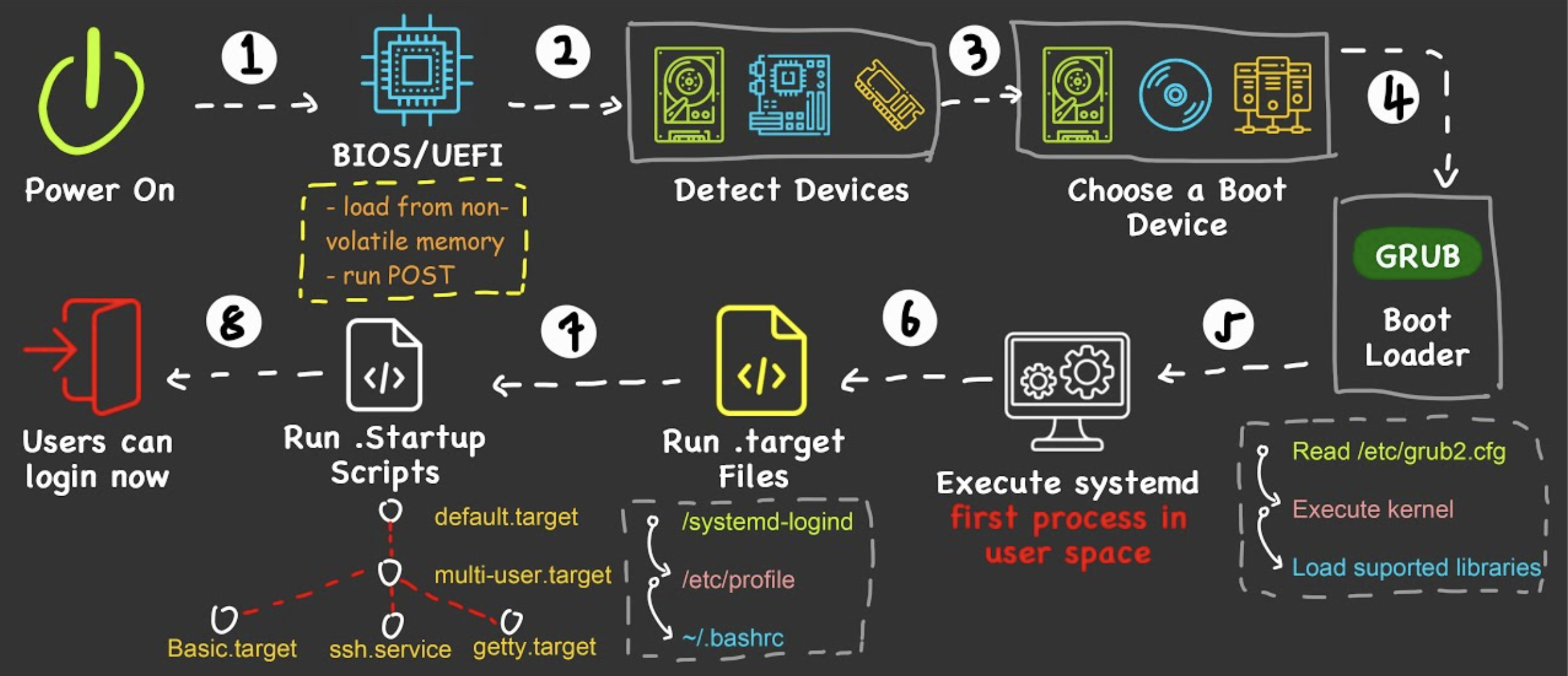
- When the power is switched on, BIOS is executed first, followed by Boot Device, lastly Kernel Booting
BIOS
-
Contains low-level IO software
-
Nowadays, stored in Flash RAM - nonvolatile & can be updated
-
The newer standard is called UEFI
-
The first program that starts when booting up a computer
- Checks Main Memory capacity
- Check IO Device
- Scanning IO Bus to detect all devices attached
- Determine the Boot Device by trying out a list of devices stored in the CMOS. (Users can press keyboard shortcut - F12, F11, Esc, F8, F9 to enter a Boot Menu and choose the boot device manually)
- The Boot loader inside the boot device will carry out the next step
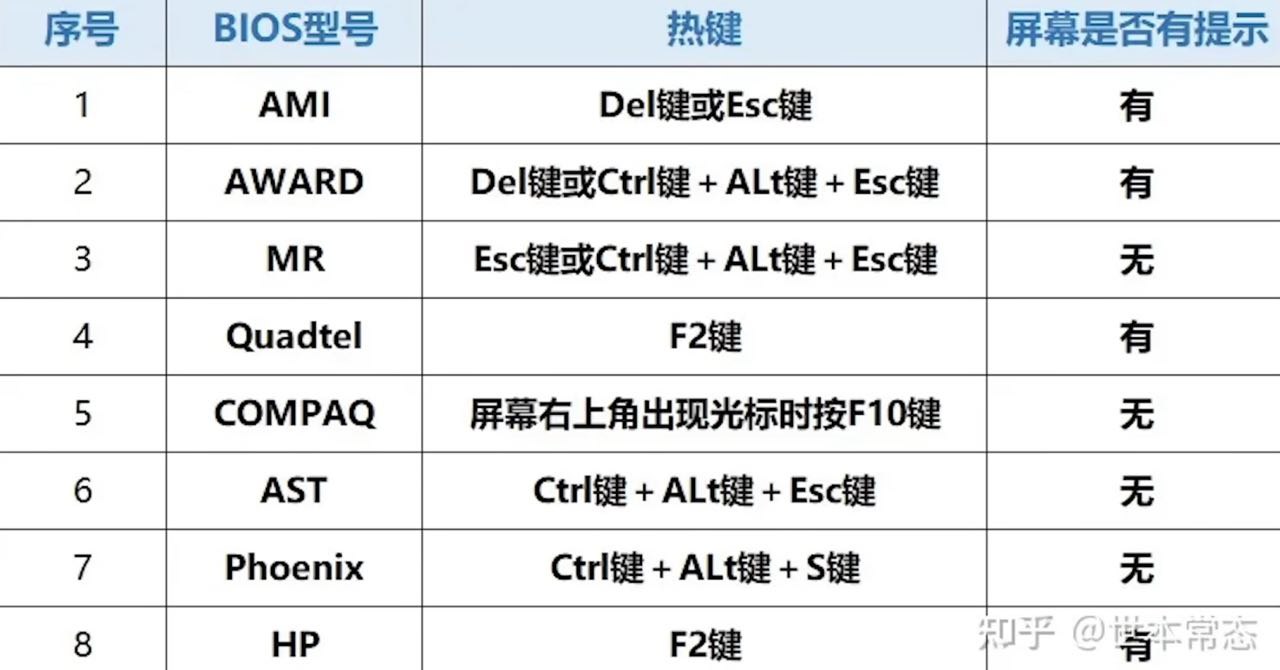
Keyboard shortcut to enter BIOS
Boot Device

- Storage device that contains Master Boot Record and the OS
- Master Boot Record is read into Main Memory to start the Boot Loader
Partition Table
Contains information about how the partitions on the disk are organized. Can be created in 2 disk partitioning schemes - Master Boot Record and GUID Partition Table (Needs UEFI BIOS)
Essential partitions of a Linux Boot Device
/bootpartition
- Stores the Linux Kernel, initial RAM disk image (initrd), and Boot loader
- 500MB - 1GB is typically sufficient
- Ext4 is a common choice, but other Linux filesystems can work too
/boot/efipartition
- EFI System Partition (ESP), stores the EFI bootloader files specifically needed for systems using UEFI (most modern systems)
- 100MB - 500MB is usually enough
- Formatted as FAT32 for compatibility across different architectures
- Needs “boot” or “esp” flag
/bootbecomes optional to unified the partition for kernel and boot loaders. However, non-encrypted/bootis required whatever the UEFI choice if the rest of the system is encrypted!
/partition (root partition)
- Core of your Linux installation. It contains all your system files, user files, program data, etc
- The space of the rest of the boot device
- EXT4 is the most common and reliable option
Optional partitions for Linux Boot Device
These optional partitions provide extra features.
/homepartition
- Keeps your user files separate from system files, you can format your
/partition without losing personal files and settings, great for Distro hopping- EXT4 for stability and reliability and XFS for big media files
linuxswappartition
- Swap Space
- Traditionally, double your RAM size was recommended. Modernly, it depends on your usage. If you hibernate often, matching your RAM size is wise. Otherwise, a few GB might suffice if you have ample RAM
- ”linux-swap” File System and no mount point
Boot loader
- Examines the partition table at the end of boot sector to determine which partition is active. Providing a menu for user to select which OS to boot
- When an OS is selected, boot loader loads in the corresponding Kernel into the Main Memory
- Kernel Booting will finish up on the booting of the OS
- One common boot loader is Grub2
References
- How Does Linux Boot Process Work?