Concurrency (并发)
Quote
Concurrency is about dealing with lots of things at once, but parallelism is about doing lots of things at once.
- A way to run multiple Thread or Process (进程) at the same time, instead of running one thread or process after another thread or process is done
- We can achieve concurrency with multiple Core, this is also known as Parallelism (并行性). We can also achieve concurrency with a single CPU core by performing Context Switch
Maximise CPU utilisation
CPU is idle when the process and thread are performing non CPU-bounded tasks like reading and writing to IO Device and waiting a result from a remote Server etc. By performing context switch, we can let another process or thread to use CPU to complete its computation. Parallelism allows us to run multiple threads of processes at the same, if we have 4 CPU cores, it means we can have 4 processes/threads consuming the CPU at the same time.
Time-Sharing
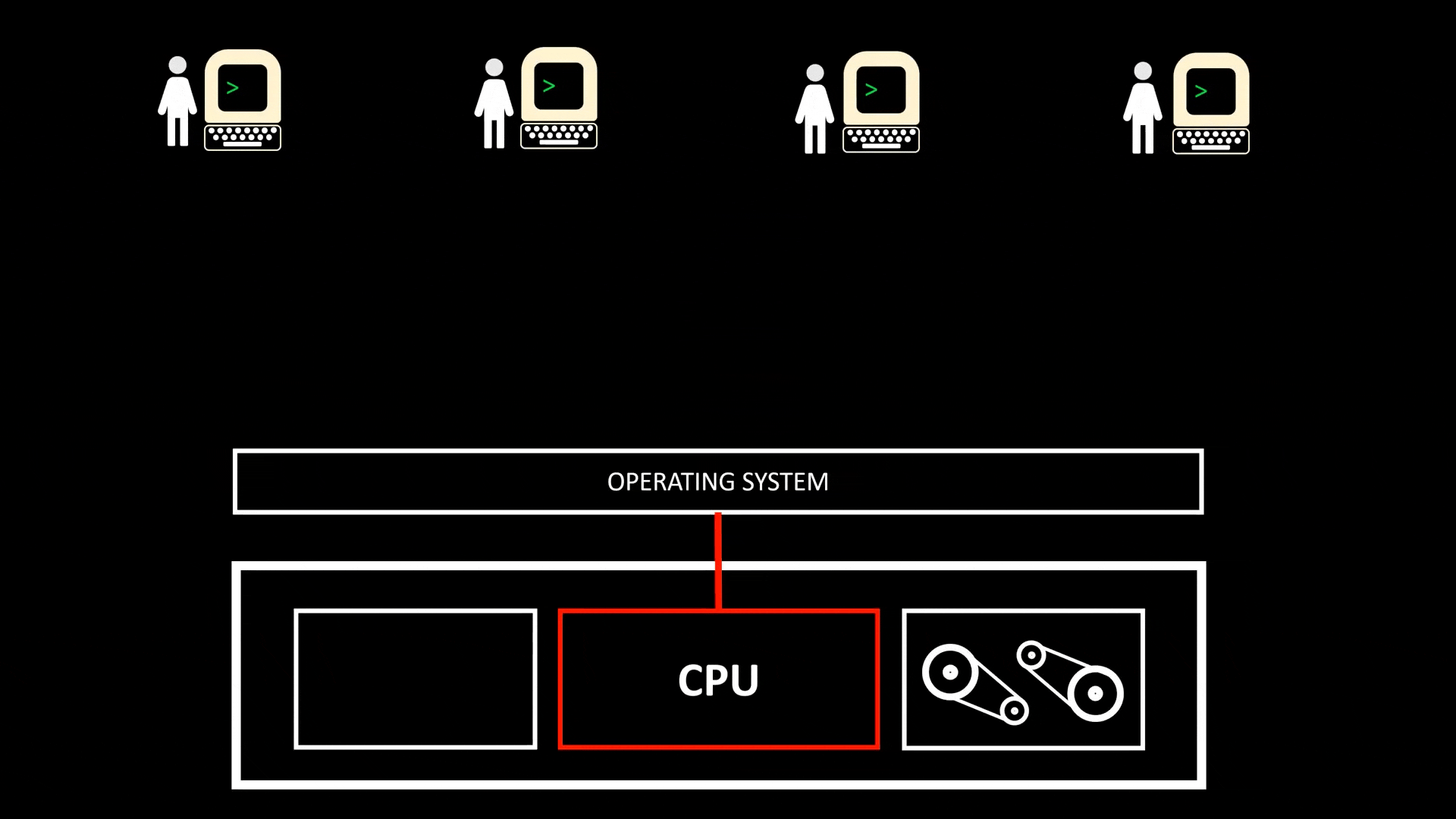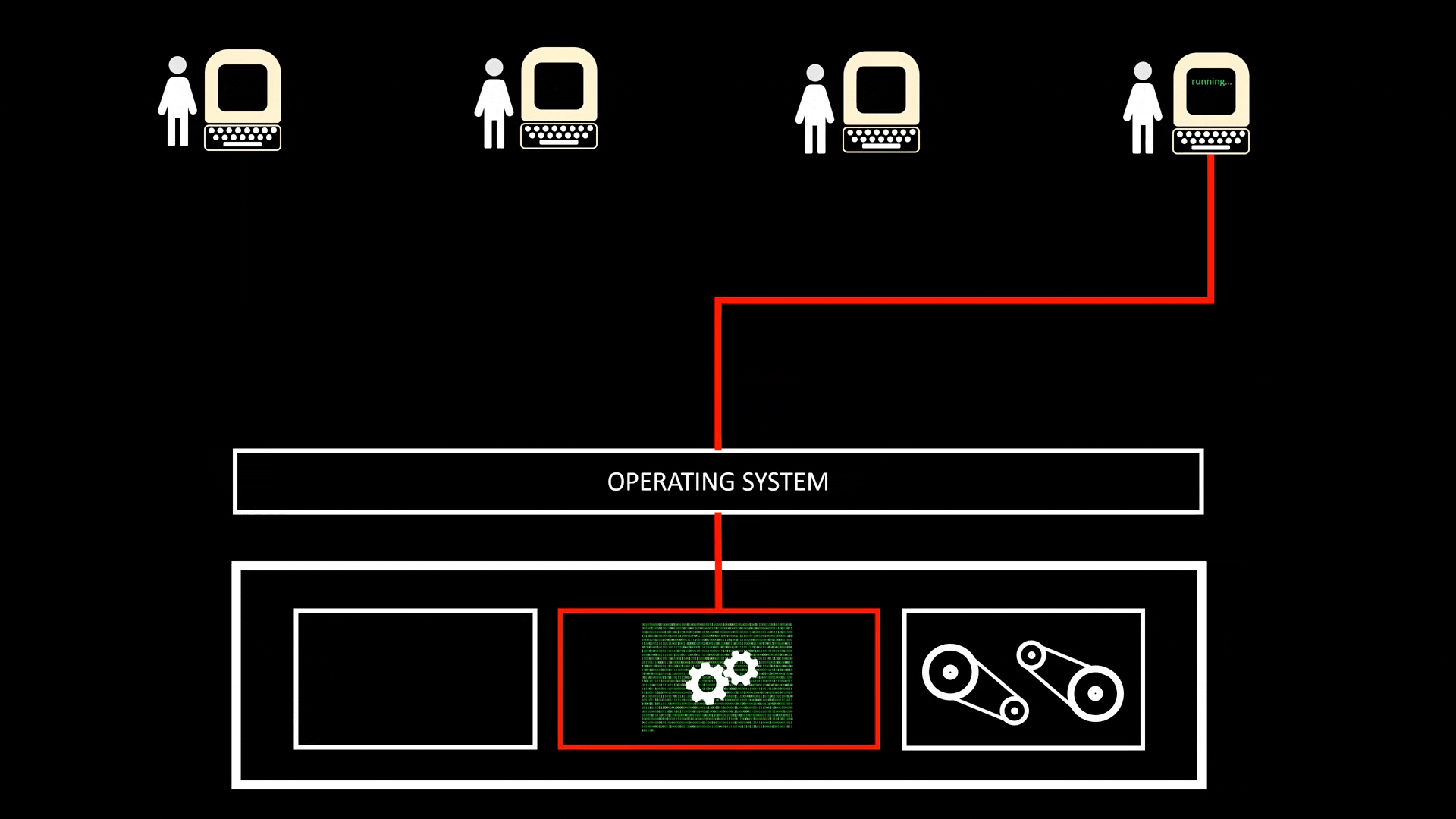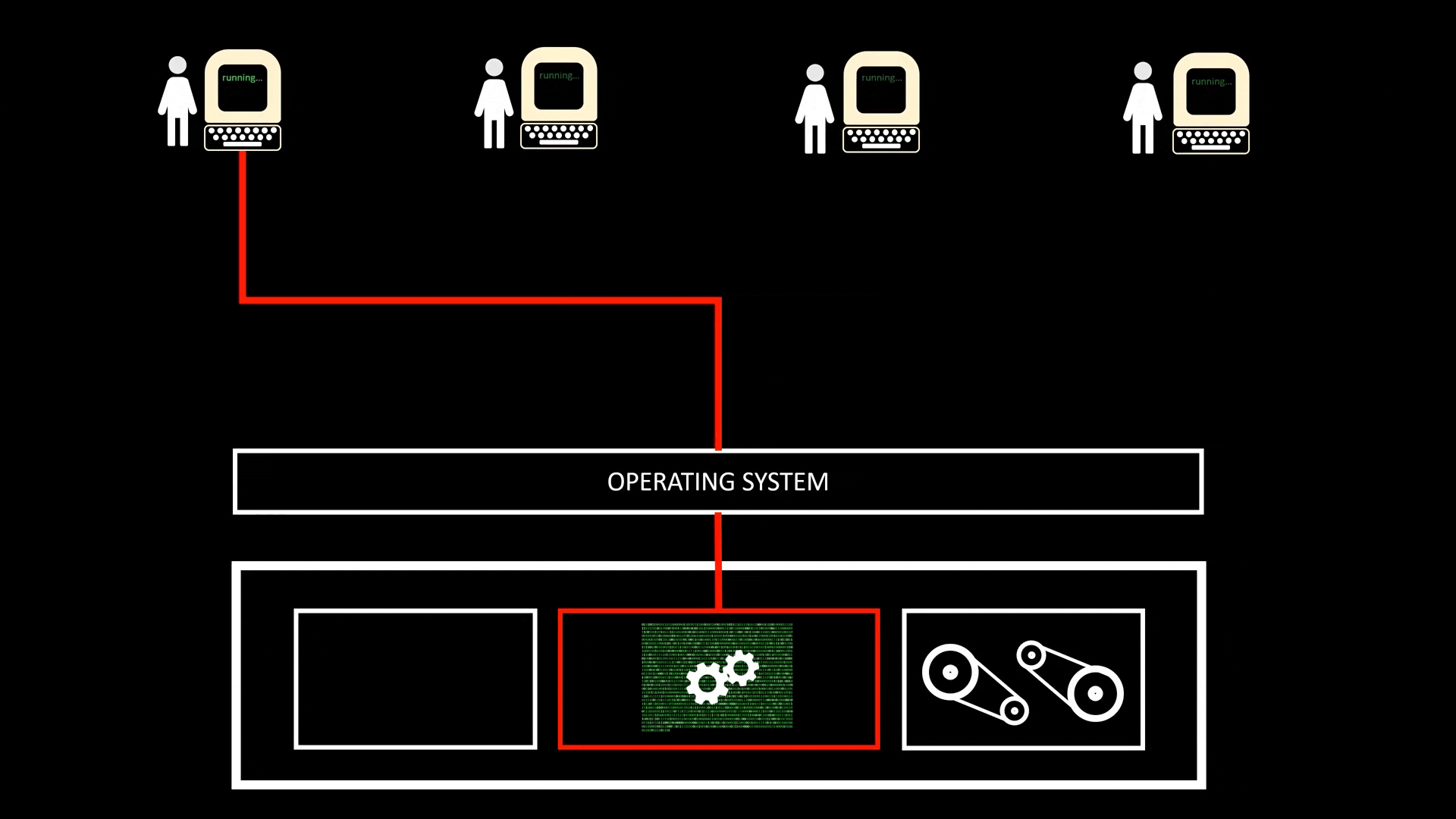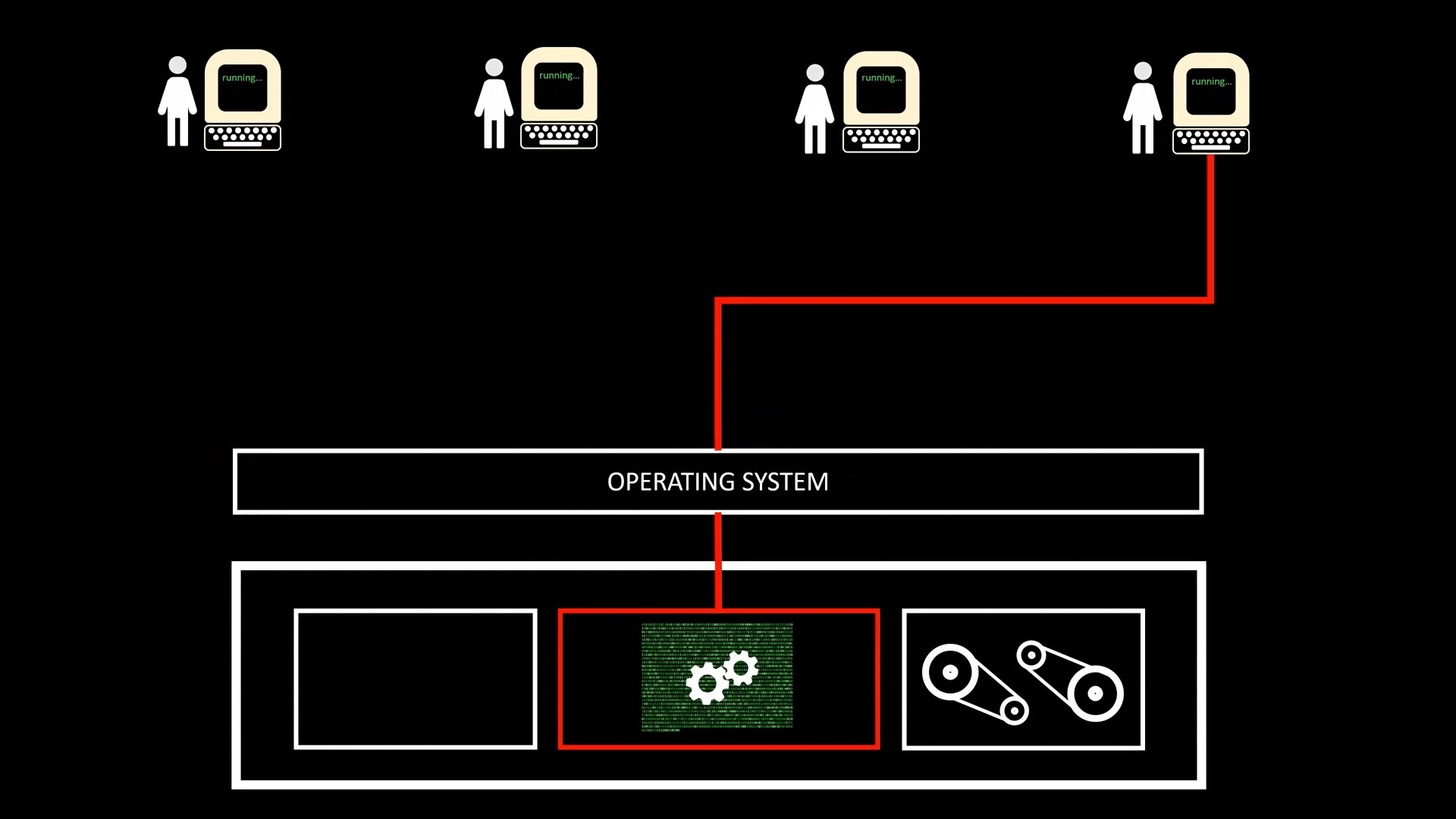
- A implementation of Concurrency (并发) and a specific implementation of Multi-tasking when CPU is shared by multiple users at the same time, achieved with quick Context Switch. This allow multiple users to run jobs on the same computer at the same time
- All Time-sharing systems are Multi-programming systems
Info
Multics - Wikipedia was one of the first time-sharing OS which inspires the creation of Unix.
Parallelism (并行性)
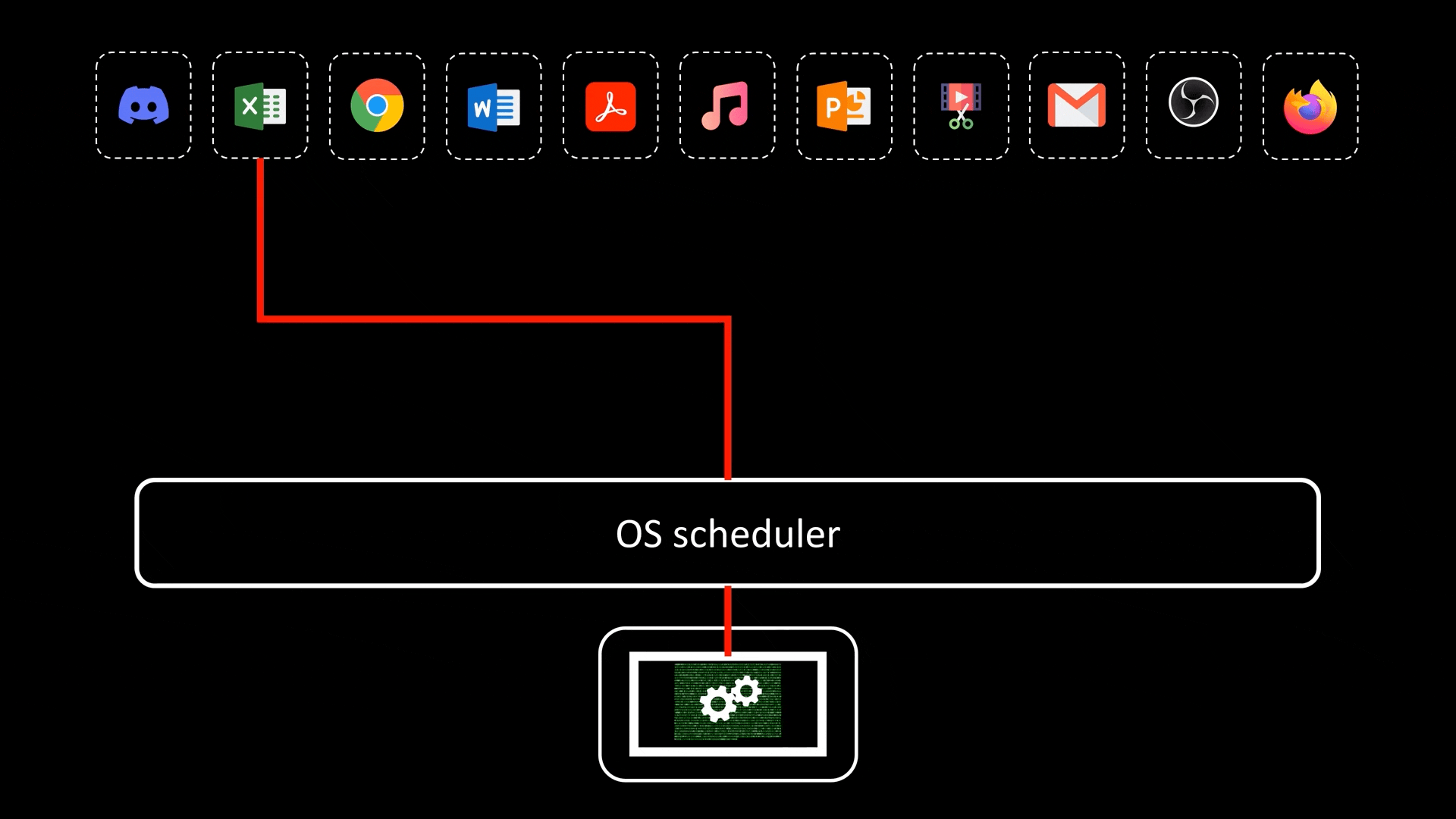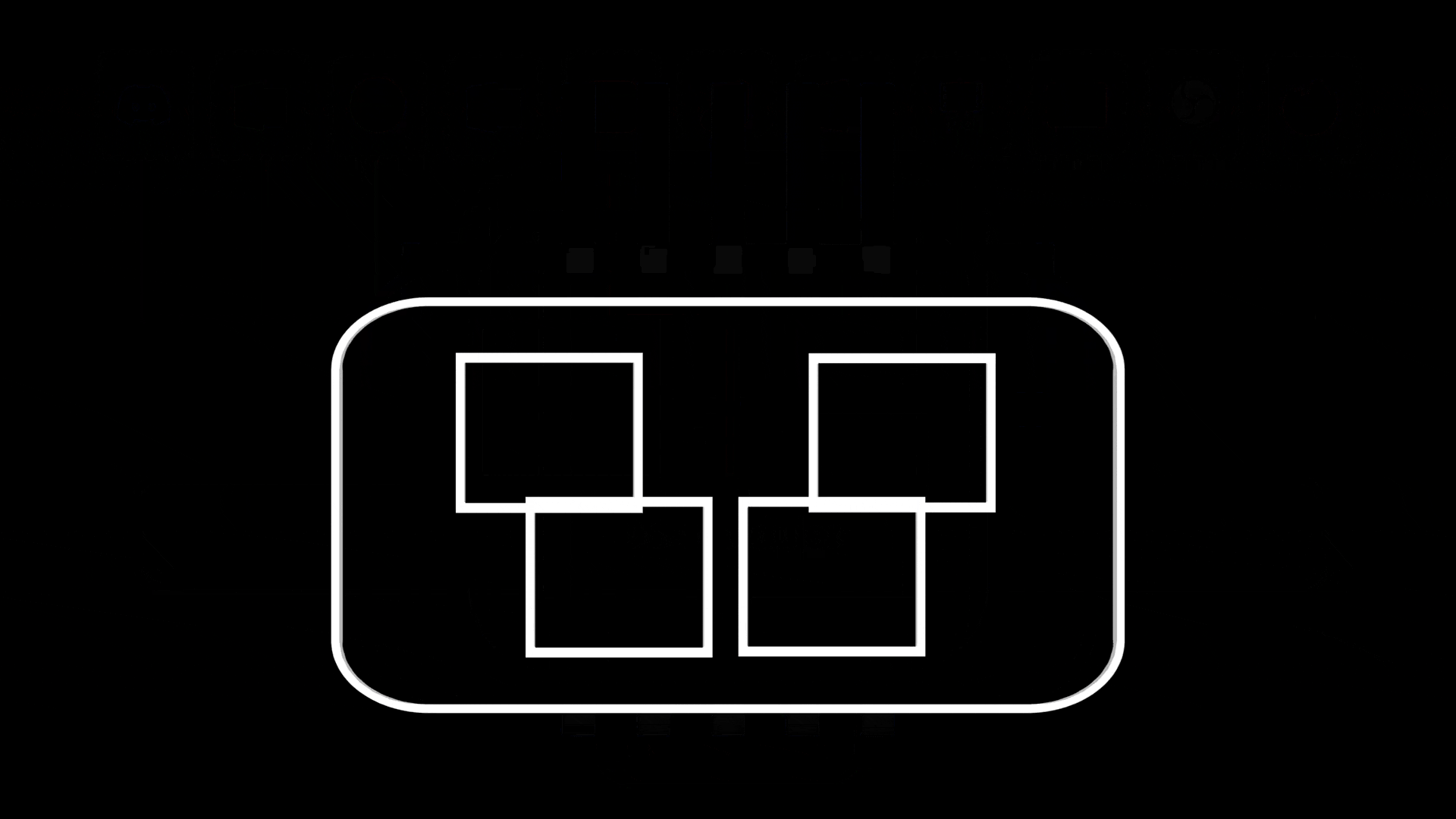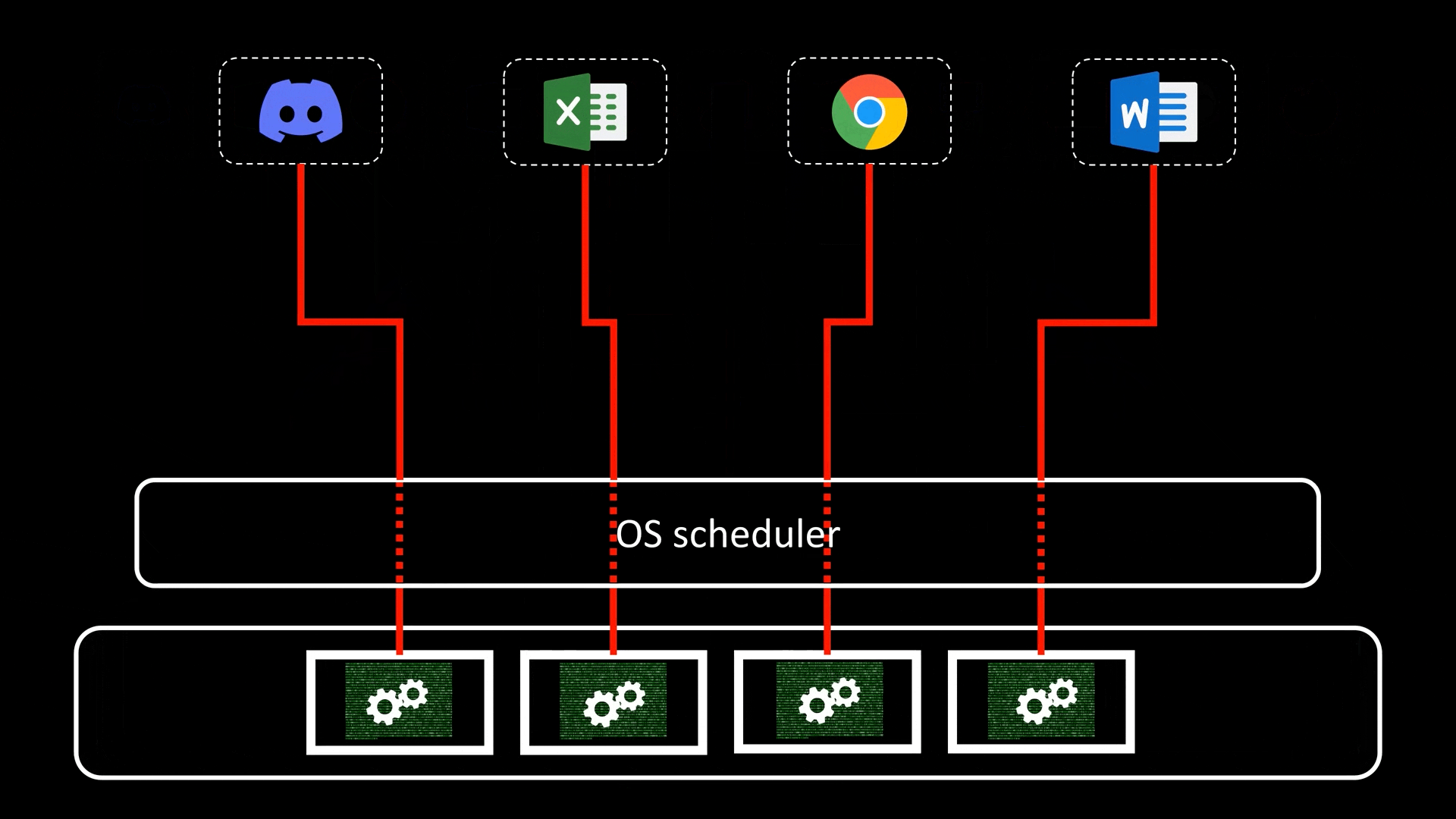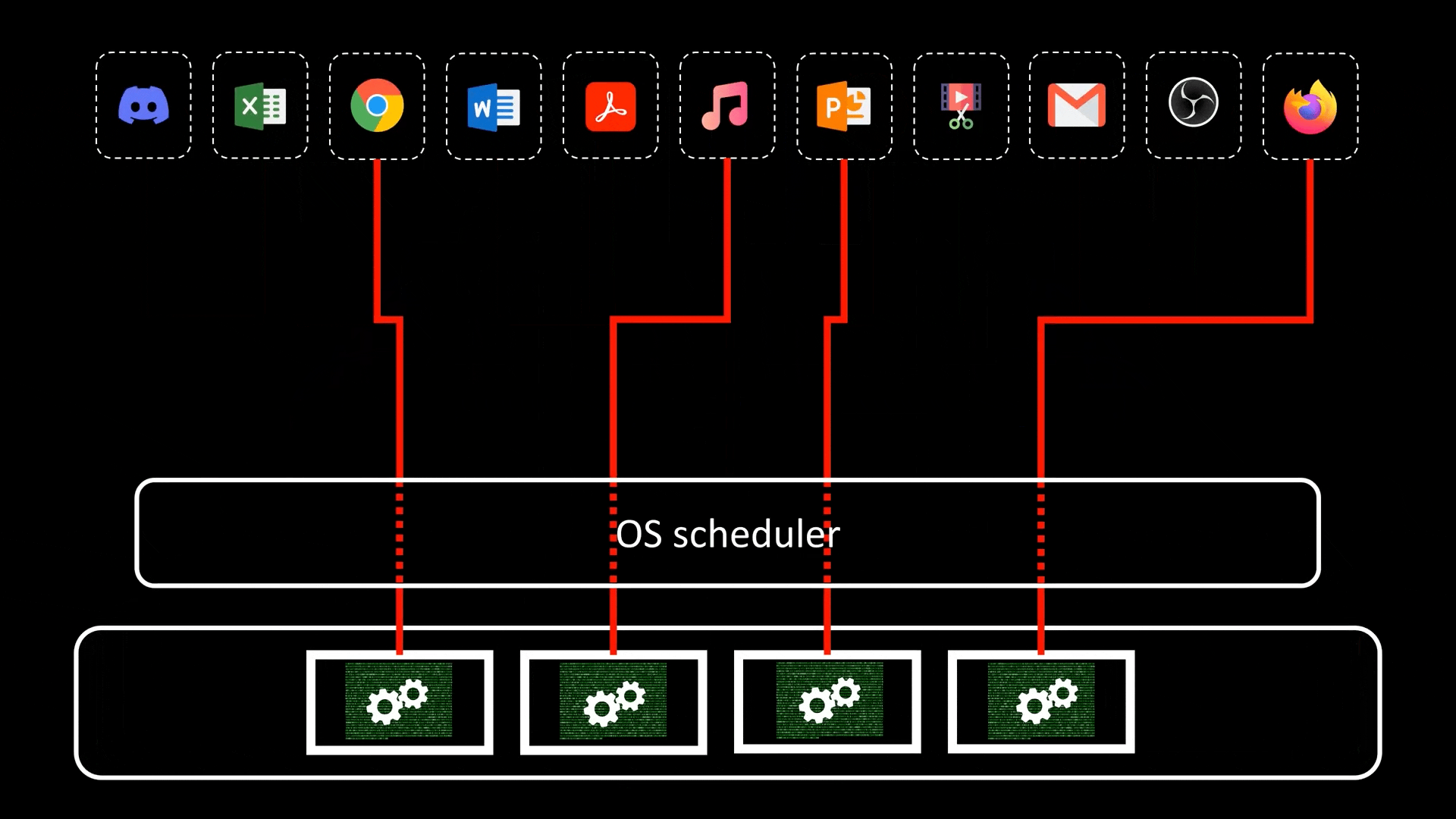
- A subset of Concurrency (并发), Process (进程) and Thread run on their own Core. This is the true processing of multiple tasks at the same time, not an illusion created by quick Context Switch
Corporative Scheduling
- Rather than the Kernel decides when to preempt a Process (进程) and pass the CPU to another process. Process passes control back to kernel for it to perform Process Management
CPU Hogging
Process can hog to CPU forever, modern OS adapts to Preemptive Scheduling instead.
Preemptive Scheduling
- Before Kernel set the Program Counter to the Instruction of a selected Process (进程), the kernel sets the Timer Chip to trigger an Hardware interrupts (外中断) after some period of time
- The kernel switches the Privilege Level to User Mode and set the program counter to the instruction of a selected process, so the process can start executing
- When the timer chip elapses, it triggers a Hardware interrupts
- The hardware interrupt invokes Trap Interrupt (陷入) which triggers the corresponding Interrupt Handler
- Interrupt handler passes control to Process Scheduler when it completes
- Process Scheduler selects a process to run by restoring the state of the CPU for that process from the process’s Process Control Block (PCB)
- Repeat step 1 to step 6
No CPU Hogging
The hardware interrupt generated by timer chip ensures the kernel obtain control to perform Process Management on a configured interval. The eliminates any process from hogging the CPU forever which may happen in the case of Corporative Scheduling.